- Published in Lancet
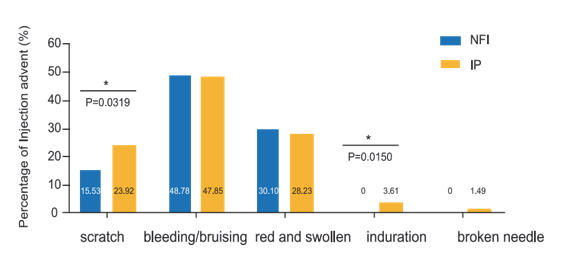
There was no new indurations observed in NIF group compared with IP.(P=0.0150) Broken needle were observed in the IP group, no risk in NIF group. The adjusted mean reduction from baseline of HbA1c 0.55% at week 16 in NFI group was non-inferior and statistically superior compared with that of 0.26% in IP group. Administration of insulin by NIF could provide better safety profile than by IP injections, by reducing skin scratches, indurations, pain and no risk for broken needles.
Introduction:
The proportion of patients with type 2 diabetes using insulin is still very low and often is initiated relatively late. Many factors were found to affect the delay in insulin use, including fear of needles, psychological disorders during insulin injections and the inconvenience of insulin injections, all of which were important reasons for patients refusing to initiate insulin treatment. In addition, injection complication such as indurations caused by long-term needle reuse can also affect the efficacy of insulin treatment in patients who have already used insulin.
The needle-free insulin injector is designed for diabetic patients who fear injections or are reluctant to initiate insulin therapy when it is clearly indicated. This study aimed to evaluate patient satisfaction and compliance with a needle-free insulin injector versus conventional insulin pen injections in patients with T2DM treated for 16 weeks.
Methods:
A total of 427 patients with T2DM were enrolled in a multi-center, prospective, randomized, open-label study, and were randomized 1:1 to receive basal insulin or premixed insulin via a needle-free injector or via conventional insulin pen injections.
Result:
In the 412 patients who completed the study, mean SF-36 questionnaire scores were increased significantly in both the needle-free injector and conventional insulin pen groups, with no significant difference between the groups in compliance. However, subjects in the needle-free injector group showed significantly higher treatment satisfaction scores than those in the conventional insulin pen group after 16 weeks of treatment.
Summary:
There are no significant difference between insulin pen and needle-free injection groups on this result of SF-36.
Needle-free injection of insulin leads to higher patient satisfaction and improved treatment compliance.
Conclusion:
He needle-free injector improved the quality of life of T2DM patients and significantly enhanced their satisfaction with insulin treatment compared with conventional insulin pen injections.
Post time: Apr-29-2022